ct guided nerve root injection
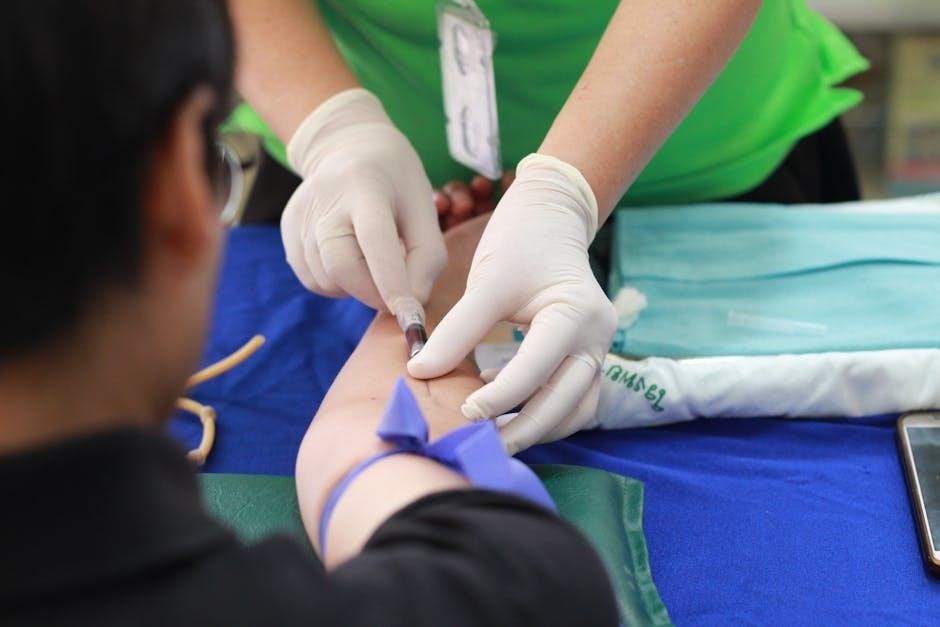
A minimally invasive procedure using CT imaging to guide the injection of medication around specific nerve roots, aiding in both diagnosis and treatment of nerve-related pain and inflammation;

Diagnostic and Therapeutic Benefits
CT-guided nerve root injections offer dual benefits, aiding in diagnosing nerve-related pain and providing therapeutic relief by reducing inflammation and alleviating discomfort through targeted medication delivery.
Diagnostic Benefits
CT-guided nerve root injections play a crucial role in diagnosing nerve-related pain by identifying the exact source of discomfort; The procedure involves injecting a local anesthetic or corticosteroid around the affected nerve root, allowing clinicians to assess pain relief and confirm the nerve’s involvement in the pain cycle. This diagnostic capability helps determine if the targeted nerve is the primary source of symptoms, such as sciatica or paresthesia. The precision of CT imaging ensures accurate placement of the injection, minimizing risks and maximizing diagnostic accuracy. By evaluating the patient’s response to the injection, healthcare providers can better understand the underlying condition and tailor further treatment plans. This approach is particularly valuable for conditions like herniated discs or spinal stenosis, where nerve root irritation is a common cause of pain.
Therapeutic Benefits
CT-guided nerve root injections offer significant therapeutic benefits by effectively reducing pain and inflammation around irritated nerves. The procedure involves injecting a combination of a local anesthetic and a corticosteroid directly into the area surrounding the affected nerve root. This targeted approach helps alleviate symptoms such as sciatica, numbness, and tingling, providing rapid and often long-lasting relief. The corticosteroid works to reduce inflammation, while the anesthetic blocks pain signals, allowing patients to regain mobility and improve their quality of life. The precision of CT imaging ensures accurate medication placement, minimizing potential risks like bleeding or infection. For many patients, this treatment delays or even avoids the need for surgical intervention. It is particularly effective for conditions such as herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and degenerative disc disease, making it a valuable option for managing chronic nerve-related pain.
Procedure Details
CT-guided nerve root injections use advanced imaging to precisely target the affected nerve root, ensuring accurate medication delivery to relieve pain and inflammation.
How the Procedure is Performed
CT-guided nerve root injections involve using computed tomography (CT) imaging to precisely locate the affected nerve root. The patient lies on a table, and the CT scanner provides real-time images to guide the physician. A local anesthetic is administered to numb the skin, and under CT guidance, a needle is inserted to the target area. Contrast dye may be used to confirm the needle’s position. Once correctly positioned, a steroid and/or anesthetic is injected around the nerve root to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain. The procedure is minimally invasive and typically performed on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to return home the same day. The use of CT imaging enhances accuracy, ensuring the medication is delivered directly to the affected area for optimal relief.
Patient Preparation
Patient preparation for CT-guided nerve root injections is crucial to ensure safety and effectiveness. Patients are typically advised to avoid eating or drinking for a few hours before the procedure, though specific instructions may vary. Comfortable clothing should be worn to facilitate easy access to the treatment area. Blood-thinning medications may need to be temporarily discontinued to minimize bleeding risks, as directed by the physician. On the day of the procedure, patients should arrive with a responsible adult to provide transportation home, as they may experience temporary numbness or weakness. Allergies, especially to steroids or contrast agents, must be disclosed beforehand. Additionally, any medications or supplements being taken should be reported to avoid complications. Proper preparation helps ensure a smooth procedure and optimal outcomes.
Post-Procedure Care
Following a CT-guided nerve root injection, patients are monitored for a short period to ensure stability. They are advised to rest and avoid strenuous activities for 24-48 hours. A responsible adult should accompany the patient home, as temporary numbness or weakness may occur. Patients should avoid driving or operating heavy machinery for at least 24 hours. Mild pain at the injection site is common and can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, unless otherwise directed by the physician. It’s important to keep the injection site clean and dry to reduce infection risk. Patients are encouraged to resume normal activities gradually and report any unusual symptoms, such as severe pain, swelling, or fever, to their healthcare provider promptly. Follow-up appointments are typically scheduled to assess the procedure’s effectiveness and address any concerns. Proper post-procedure care helps maximize outcomes and minimize potential complications.

Indications for CT-Guided Nerve Root Injections
CT-guided nerve root injections are primarily indicated for treating chronic pain, inflammation, and nerve irritation, particularly in the neck, back, and legs, providing both diagnostic and therapeutic benefits.
Conditions Treated
CT-guided nerve root injections are commonly used to treat various conditions causing nerve-related pain and inflammation. These include sciatica, paraesthesia, and facet joint pain. They are effective for alleviating pain caused by herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and spondylitis. The procedure is also beneficial for treating inflammatory conditions affecting the nerve roots, such as radiculitis or neuropathy. Additionally, it is used to manage chronic pain resulting from nerve irritation or compression in the cervical, lumbar, or thoracic regions. By targeting the specific nerve root, the injection helps reduce inflammation and relieve pain, improving mobility and quality of life for patients with these conditions.
Contraindications
CT-guided nerve root injections are not suitable for all patients and have specific contraindications. Absolute contraindications include active infections, severe allergic reactions to the medications used, and bleeding disorders or anticoagulant therapy, which increase the risk of hemorrhage. Relative contraindications may include pregnancy, as the risks to the fetus must be carefully weighed, and unstable medical conditions such as uncontrolled diabetes or high blood pressure. Patients with implanted medical devices, such as pacemakers, may also face limitations due to the CT imaging process. Additionally, severe obesity or anatomical abnormalities may hinder accurate needle placement under CT guidance. Each patient’s suitability for the procedure is evaluated on a case-by-case basis, considering their overall health and specific conditions.
Risks and Complications
CT-guided nerve root injections carry risks, including pain at the injection site, inflammation, and allergic reactions. Rare but serious complications may involve infection, nerve damage, or bleeding.
Common Risks
Common risks of CT-guided nerve root injections include pain at the injection site, swelling, or temporary discomfort. Some patients may experience inflammation or allergic reactions to the medications used. Additionally, there is a small risk of bleeding or bruising at the injection site. In rare cases, patients might feel lightheaded or dizzy immediately after the procedure. These side effects are typically mild and resolve on their own within a few days. Proper patient selection and adherence to sterile technique help minimize these risks. While the procedure is generally safe, it is important for patients to discuss their medical history and any concerns with their healthcare provider beforehand to ensure the best outcome.
Serious Complications
While rare, serious complications of CT-guided nerve root injections can occur. These may include infection at the injection site, nerve damage, or unintended injection into a blood vessel. Infection, though uncommon, can lead to abscess formation or meningitis if not promptly treated. Nerve damage might result in numbness, weakness, or paralysis in the affected area. Steroid medications, often used in the injections, can cause systemic side effects in rare cases, such as adrenal insufficiency or increased blood sugar levels in diabetic patients. Additionally, bleeding complications, including hematoma formation, are possible, especially in patients on anticoagulant therapy. These serious complications underscore the importance of proper patient selection, adherence to sterile technique, and careful monitoring post-procedure. Patients should immediately report severe symptoms, such as worsening pain, fever, or neurological deficits, to their healthcare provider.